| Vocademy |
What is an electrical circuit
A pneumatic (compressed air) circuit
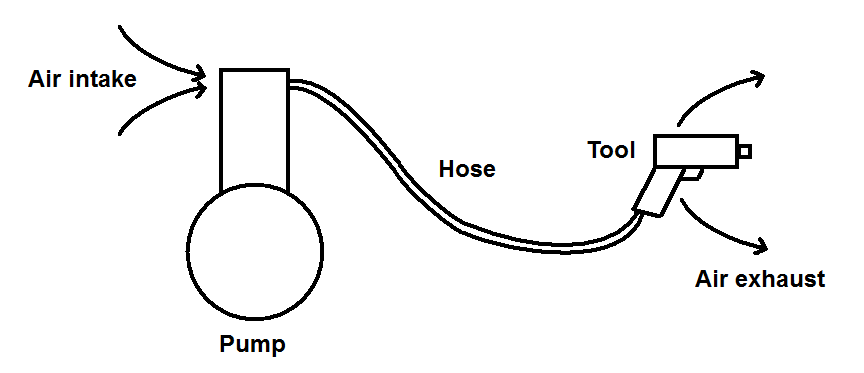
Electricity is a lot like compressed air. For example, a mechanic uses compressed air to operate tools. A pump sucks air in one side and forces it out the other side under high pressure. A hose carries the air to the tool where the pressurized air is used to turn a spindle (as in an air wrench) or to push a piston (as in a jackhammer). After doing its work, the air returns to the atmosphere. The air makes a circuit from the atmosphere, through the pump, through the hose, through the tool and back to the atmosphere[1].
 |
|
A Pneumatic Circuit
A pump sends high-pressure air through a hose to a pneumatic tool. The path of the air—from the atmosphere, through the pump, the hose, the tool and back to
the atmosphere—creates a circuit through which the air circulates.
|
An electrical circuit
In metals, there are gazillions of
electrons that are free to move around and, although confined to the
metal, act a lot like the air molecules around us. If we make a wire
out of metal, that wire becomes a lot like the air hose in the
illustration above. If we connect each end of the wire to opposite ends
of a battery, the battery will act like a pump. This creates an
electrical circuit where electrons are sucked in the positive side of
the battery and forced out the negative side. The electrons travel
around the wire back to the positive side. The battery acts like a pump
and the wire acts like a hose or pipe through which the electrons can
flow around the circuit.
 |
|
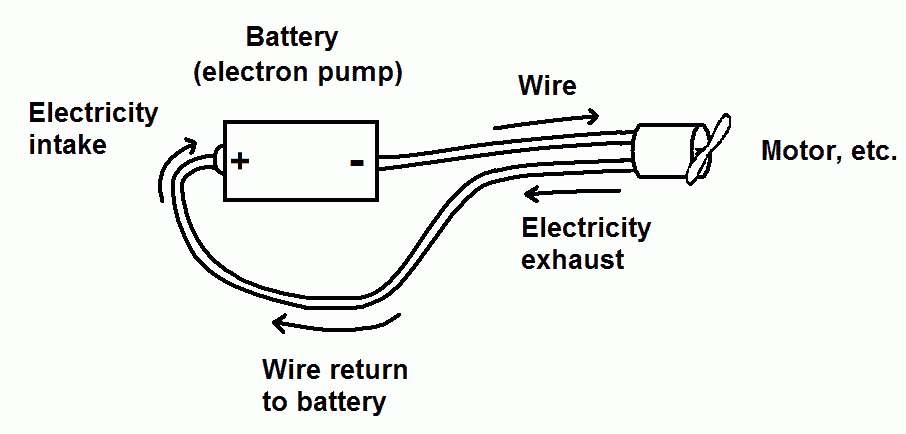
An Electric Circuit
A battery acts like a pump and sends high
voltage electrons (electrons under high electrical pressure) through a
wire. The path of the electrons, from the negative terminal of the
battery, through the wire, through one or more devices (such as a motor) and back to the positive terminal creates a
circuit through which the electrons (electricity) circulates.
|
All we need now is something to pump
the electricity through where it can do something useful. For example,
we could pass the electricity through a coil of tungsten wire. If we
pump enough electrons through that wire, it will heat up until it glows
white hot. Put that tungsten wire in an evacuated glass container so
that it won't burn up and you have a light bulb.
With a compressed air system, we pump
air through tools to do something useful. With electricity, we pump
electrons through electrical devices to do something useful. In either
case, the fluid (air or electricity) makes a circuit. In a compressed
air system a pump circulates the air around the circuit and in an
electric circuit a battery pumps electrons around the circuit.
A refrigerations system
Another good analogy of an electrical circuit is a refrigeration system, like the one illustrated below.| High pressure |
 |
Low pressure |
|
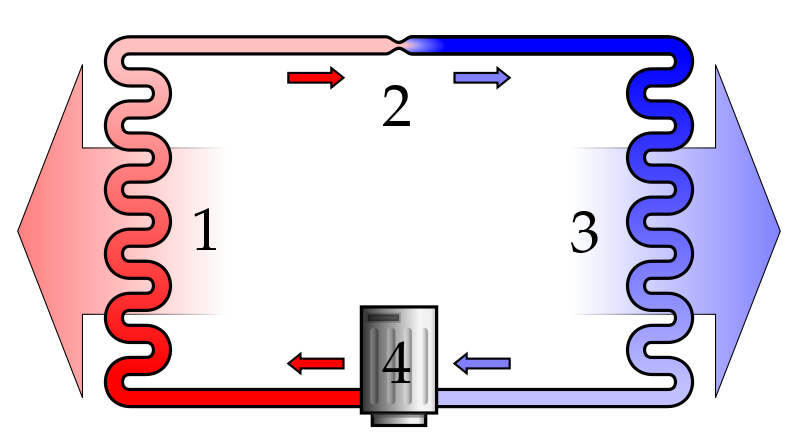
A
Refrigeration System
The pump (4) circulates the refrigerant. The refrigerant backs up when it encounters the restriction (2) increasing the pressure on the left side of the system (1). The high-pressure side of the system gets hot and air is blown across it to remove heat. After the refrigerant passes the restriction, the pressure drops. Expanding refrigerant in the low-pressure side (3) cools. Air is blown across the cool refrigerant tubes to cool the surroundings. |
A refrigeration system is an even
better analog of an electrical circuit than a compressed air system. A
refrigeration system is a closed system. It circulates the same fluid
over and over again. An electrical circuit is
also a closed system since the electrons cannot leave the system[2].The
refrigeration system also clearly shows what happens when you restrict
the flow of a fluid. It causes a sharp differential in the pressure
from one side of
the restriction to the other. It's like blocking a garden hose with
your thumb; the pressure increases behind your thumb in the hose. If
you partially block the flow of a fluid, you will get a backup of
pressure where the fluid encounters the blockage and a drop in pressure
on the opposite side of the blockage.
Another electrical circuit
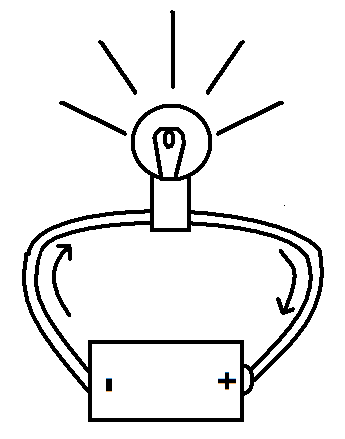
In the following diagram, we have rotated the electric circuit to compare it to the refrigeration system above.|
|
Light bulb acts
as a restriction |
|
| High voltage |
 |
Low voltage |
|
An
Electrical Circuit
The battery circulates the electricity (clockwise). The electricity backs-up when it encounters the light bulb causing a relatively high voltage on the left side of the circuit. After the electricity passes through the light bulb, the voltage drops. The right side of the circuit has a low voltage just as the right side of the refrigeration system has a low pressure. |
A light bulb, like any other
electrical component, offers resistance to the flow of electricity.
When flowing electrons encounter the light bulb in the above circuit,
there is a backup of voltage. There is a correspondingly lower voltage
where the electrons exit the light bulb (more about this in
Resistors). In a complex electronic
circuit, there are many components with electrical current flowing
through them. Each one has a corresponding voltage differential across
it. A large part of the art of electronic engineering is manipulating
these changes in voltage and the related electrical currents.
Pneumatic and electrical components
The following table lists several pneumatic devices, what they do and their electrical equivalents. We will discuss these devices in detail later.|
Pneumatic Device |
Action |
Electronic
Equivalent |
|
Pipe |
Provides a conduit
for fluid to flow through. |
Wire |
|
Pump |
Sucks fluid in one
end and blows it out the other (circulates the fluid around the
circuit). |
Battery or Generator |
|
Valve |
Blocks or unblocks
the flow of air. |
Switch |
|
Check valve |
Allows air flow in
one direction only |
Diode |
|
Relay valve |
An air-controlled valve. A small volume of air
opens the valve, which then passes a large volume of air. |
Transistor |
|
Air tank |
Stores compressed
air. As more air is pumped into the tank, the pressure increases. |
Capacitor |
|
Restriction |
Impedes current flow.
A pressure differential develops across the restriction—higher pressure
on the side toward the source of the current—lower pressure on the side
away from the source of the current. |
Resistor |
Page summary:
- An electrical circuit is like a compressed air system.
- A battery acts like a pump
- Wires act like hoses
- Electrical components act like air tools, etc.
- An electrical circuit is a closed system
- Electricity cannot escape into the atmosphere as compressed air can.
- Restrictions in a circuit cause a pressure differential across the restriction
- A partial blockage in a compressed air system, refrigeration system or electrical circuit causes a backup of pressure (higher pressure) where the fluid encounters the blockage and a lower pressure on the opposite side of the blockage.
- Manipulating the interaction of flowing electricity and such restrictions is a large part of what electrical engineering is.
What is an Electrical Circuit
What is an Electrical Circuit Q and A
Why Don't Batteries Discharge When you Touch Them End to End
| Vocademy |
